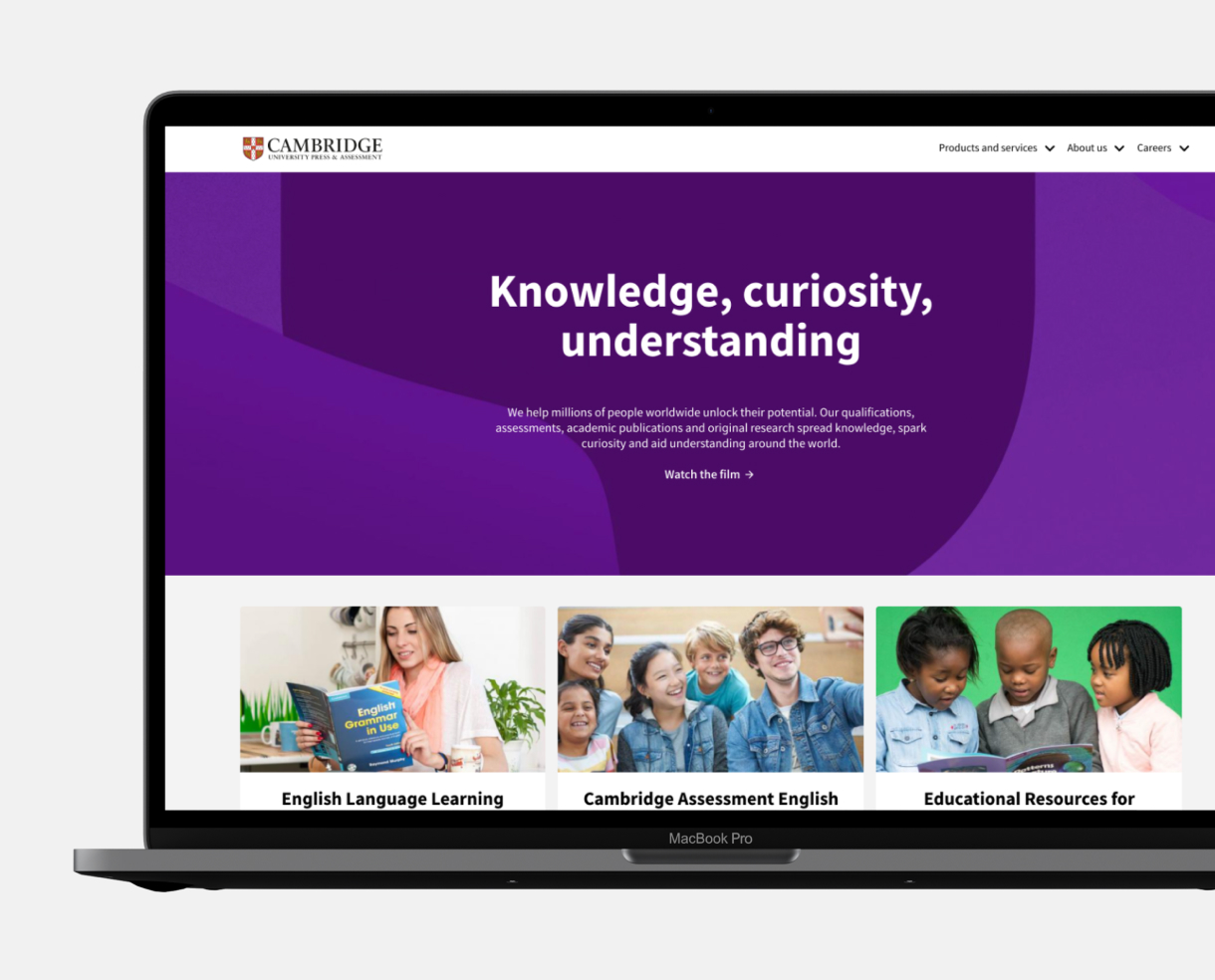
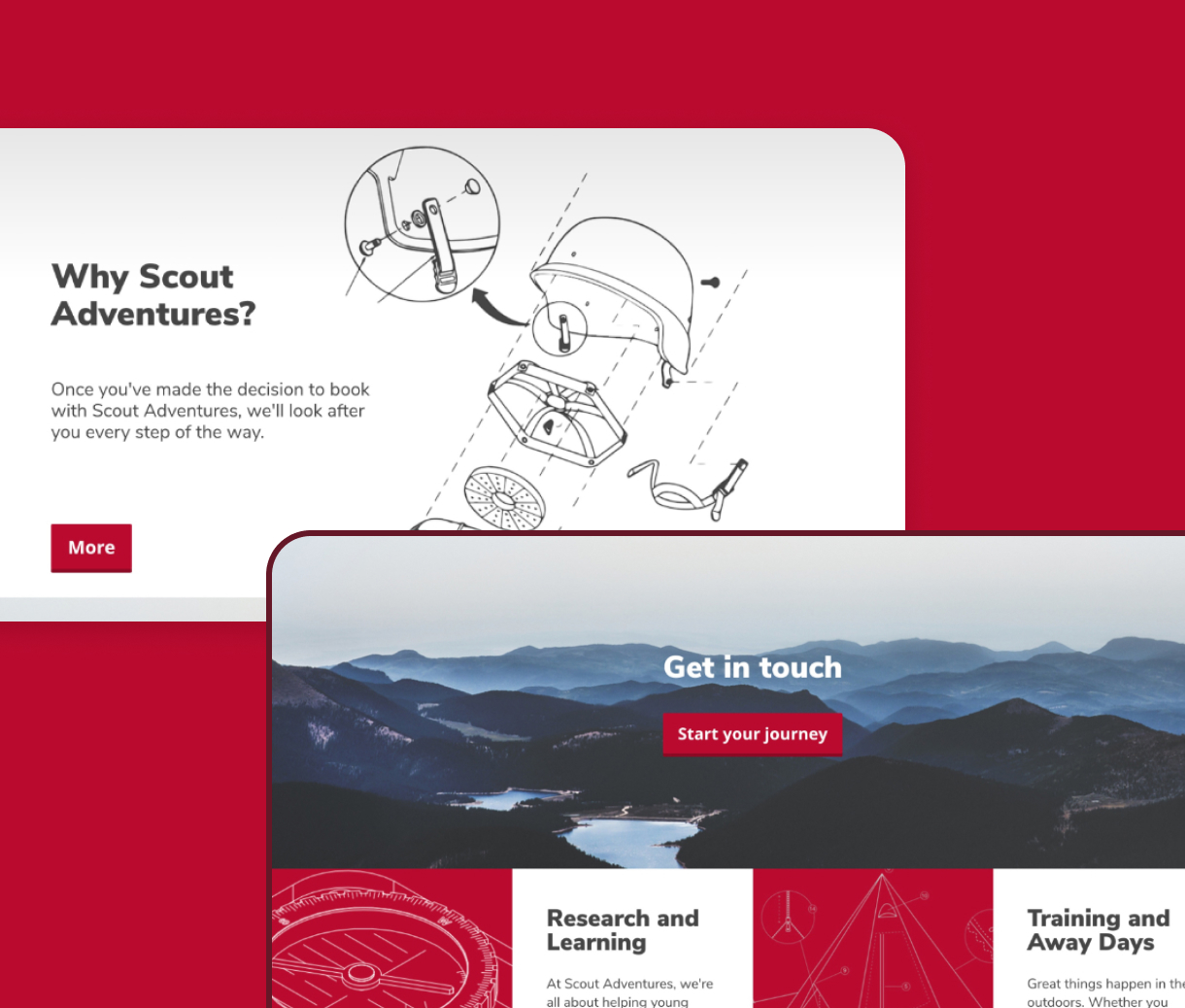
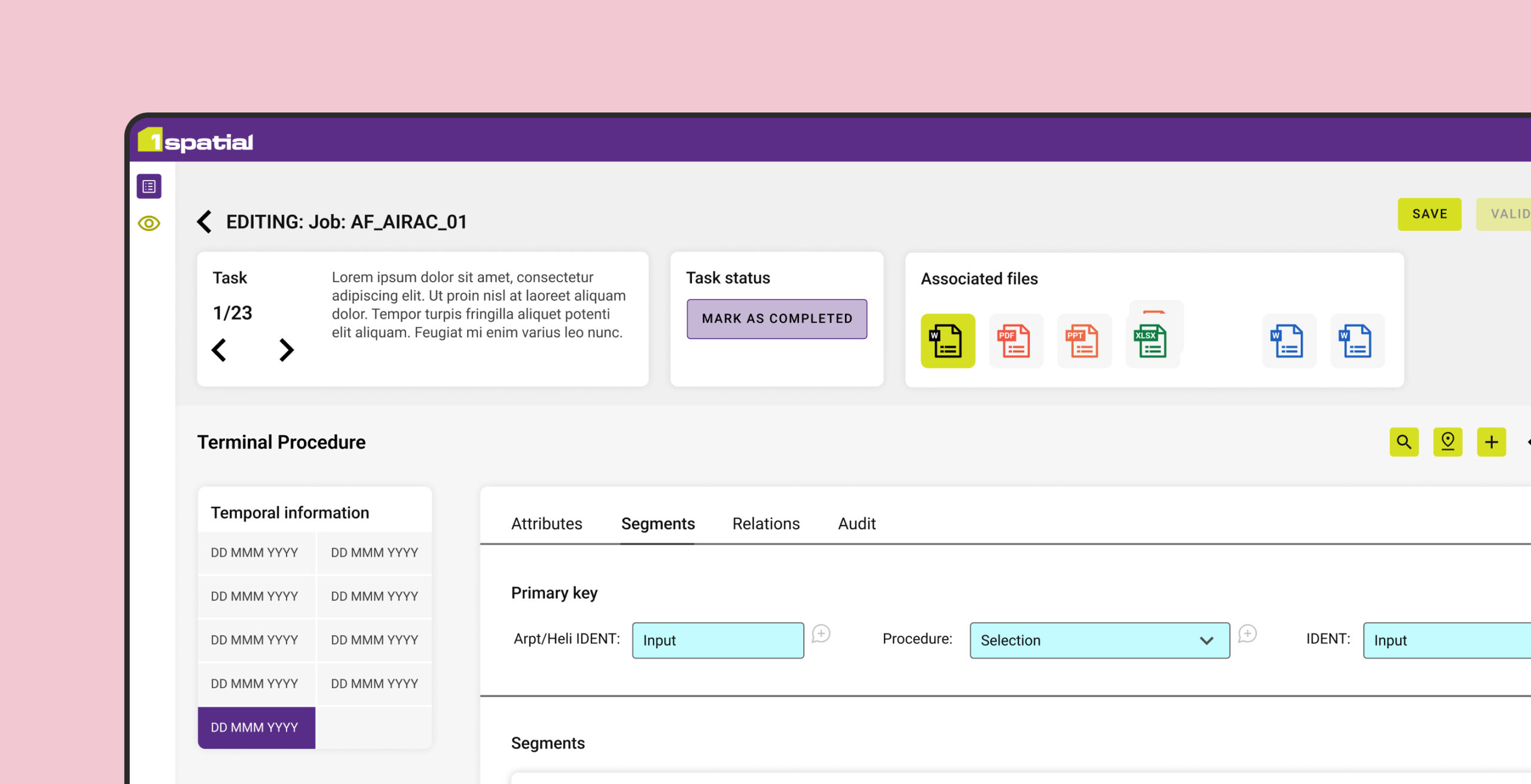
UI design services
User Interface (UI) design goes beyond aesthetics; it’s the art of crafting the visual essence of an interface. Centred on styling and interactions, UI is the canvas where your digital product or service comes to life. It’s not just an opportunity; it’s a gateway to elevate your product, creating an immersive and delightful experience for your users.

User Interface (UI) design is a crucial part of the design process; it creates the visual touchpoint through which a user interacts with a product, and it is essential to ensure users have a seamless user experience. The UI design is not just about the look; it’s about fostering a connection between users and the product, ensuring every interaction is effortlessly engaging and user-centric.
Introduction to UI design
UI design is essentially the creation of the look and feel of a product. It covers both visual and interactive elements, this includes core elements such as colour, typography, and graphic elements, as well as navigational and informational components, buttons, icons, and more. It defines not only what these components and elements look like but also how they communicate key interactions to the user throughout their engagement with the interface.
Why is User Interface design so important?
UI design helps to provide the necessary context to enable users to interact with a digital product intuitively. Without UI design you can have the best product in the world, but if a user is unable to successfully interact with its interface, it is useless. Poor user interface (UI) design can have far-reaching consequences, detrimentally affecting the overall user experience and a product’s success. The negative impacts extend to brand perception, as users may associate a poorly designed interface with a lack of professionalism or competence. Accessibility oversights can lead to exclusion of users with disabilities, inviting legal challenges and limiting the potential user base. Increased error rates, limited user engagement, and higher bounce rates further exacerbate the challenges. In an era where user expectations are high, subpar UI design not only risks user dissatisfaction but also places a product at a competitive disadvantage, potentially affecting market share and overall success.
The role of UI in UX design
User Experience (UX) and User Interface (UI) design are integral components of the product design process, working in tandem to deliver outstanding user experiences. UX design takes the lead at the inception of the product design lifecycle, placing a paramount emphasis on comprehending and enhancing the overall user journey. It delves into users’ desires, needs, and pain points, aiming to create a holistic experience that aligns seamlessly with user expectations.
UX designers employ various research methods, such as user interviews, usability testing, and user personas, to gain deep insights into the target audience. Through this understanding, they craft user flows, wireframes, and prototypes that prioritise functionality, efficiency, and satisfaction. UX design is about orchestrating a cohesive and intuitive journey, ensuring users can effortlessly navigate, understand, and accomplish their goals within the product.
On the other hand, UI design steps in to give a tangible form to the user experience envisioned by UX. While UX focuses on the broader user journey, UI zeroes in on the aesthetics and the overall feel of the interface. UI designers meticulously curate the visual elements—colour schemes, typography, icons, and imagery—to create an aesthetically pleasing and cohesive design that resonates with the brand identity and enhances the overall user experience.
In essence, UX and UI are interdependent, each influencing and shaping the other throughout the design process. An exceptional user experience arises when the insights gained through UX research seamlessly translate into a visually appealing and user-friendly interface through the efforts of UI design. The synergy between these disciplines is crucial for creating digital products that not only meet user expectations but exceed them, fostering satisfaction, engagement, and long-term user loyalty.
The core elements of UI design
The core elements of UI (User Interface) design encompass various visual and interactive components that contribute to creating a user-friendly and aesthetically pleasing interface. Here are the key elements:
- Layout: the arrangement and organisation of interface elements, including spacing, alignment, and overall structure.
- Typography: the selection and styling of fonts used for text elements, ensuring readability and visual hierarchy. You can find out more about the principles involved in typography in this article.
- Colour: the palette of colours used in the interface, influencing the overall look and feel and contributing to brand identity. Learn more here about the impact of colour theory on user experience.
- Images and icons: visual elements such as images, icons, and illustrations that enhance understanding and add visual interest.
- Buttons: interactive elements that prompt user actions, such as buttons, links, and CTA buttons.
- Forms and input fields: components that collect user input, including form fields, checkboxes, radio buttons, and dropdowns. In this article, we explore how to create world-class forms.
- Navigation: the system of menus, navigation bars, and links that guide users through the interface and help them locate information.
- Feedback and notifications: visual and interactive cues that inform users about the outcome of their actions or provide feedback on the system’s status.
- Microinteractions: small, subtle animations or visual responses to user actions, enhancing the overall user experience.
- Adaptive design: designing interfaces to adapt seamlessly to different screen sizes and devices, ensuring a consistent experience across platforms.
- Accessibility: designing with consideration for users with disabilities, ensuring that the interface is usable for everyone.
- Loading and progress indicators: visual cues that indicate the loading process or the progress of a user action to manage user expectations.
These elements work collaboratively to shape the user interface, creating an engaging and intuitive environment for users to interact with digital products and services.
Supporting your users' needs
Excite and engage users
Enhance usability
Improve customer retention
Improving customer retention through UI
Improving customer retention is intricately tied to the fundamental principles of UI design, particularly in its ability to cultivate user confidence through intuitive and thoughtful design elements. When a user encounters an interface that is not only aesthetically pleasing but also logically organised and easy to navigate, it instils a sense of trust and confidence. Intuitive design choices, such as clear call-to-action buttons, straightforward navigation menus, and easily understandable icons, contribute to a seamless user experience. Users are more likely to stay engaged with a product when they feel confident in their ability to navigate and interact with it effortlessly. For instance, an e-commerce platform with a user-friendly checkout process and a well-designed product catalogue can boost user confidence, reducing friction and increasing the likelihood of repeat transactions.
The correlation between UI design and customer loyalty becomes evident as users consistently interact with a product that meets their expectations and provides a positive experience. Consistency in UI design across various touchpoints fosters familiarity, reinforcing the brand identity and creating a sense of loyalty among users. Brands that prioritise strong UI design principles, ensuring a cohesive and enjoyable user journey, often find that their customers become not just one-time users but long-term advocates. Loyalty is established when users consistently find value in the product’s functionality and enjoy a visually pleasing and hassle-free experience. In essence, UI design serves as a key driver in building and sustaining customer loyalty by fostering a positive, reliable, and user-centric relationship between the user and the digital product.
The benefits of strong UI design
Strong UI design brings a multitude of benefits to a digital product, starting with its profound impact on enhancing user experience and instilling confidence among users. Through intuitive and visually appealing interface elements, strong UI design simplifies navigation and interaction, ensuring users can effortlessly understand and utilise the product’s features. This clarity and ease of use contribute to a positive user experience, fostering a sense of comfort and trust. For instance, well-designed buttons, clear typography, and a thoughtfully organised layout can guide users seamlessly, reducing the likelihood of confusion or frustration.
Moreover, the influence of strong UI design extends to customer retention and the overall reputation of the product. A visually polished and user-friendly interface creates a memorable and enjoyable experience, making users more likely to return to the product. Consistency in design elements across the interface builds familiarity and reinforces the brand identity, which is instrumental in retaining a loyal user base. For instance, a mobile app with an easy-to-navigate menu and aesthetically pleasing visuals can enhance user satisfaction, encouraging users to stick with the app over time.
Additionally, the positive user experiences facilitated by strong UI design contribute to a favourable product reputation. Users are more likely to recommend and speak positively about products that provide a seamless and enjoyable interface. Positive word-of-mouth and reviews can significantly enhance the product’s reputation in the market, attracting new users and solidifying the product as a trustworthy and user-centric solution. In summary, strong UI design not only elevates the immediate user experience but also plays a crucial role in customer retention and shaping the overall perception and reputation of the product in the competitive landscape.
What’s included
We develop UI designs, interactive principles and style guides based on the wireframes and user insights we have gathered in the initial part of the design process, and we base the UI designs on your brand guidelines. If these are not yet developed or ready for a refresh, we can complement our UI work with our digital product branding package to develop a robust brand identity.

Why choose Make it Clear
At Make it Clear, we take an evidence-based approach to everything we do. Understanding your organisation, audiences, and the context in which they interact is paramount to the way we work and deliver a best-in-class user experience.
Why not consider supporting your UX and UI requirements with a design retainer?
A design retainer is a contractual agreement between Make it Clear and your company, ensuring access to our design services over a designated period. This arrangement offers a streamlined and cost-effective solution tailored to consistently meet your needs. Discover more about our design retainer services on our dedicated page.